Last week’s article discussed Lake Chad’s environmental conditions, focusing on the causes and consequences of the lake’s significant reduction in past decades. As a source of life for the surrounding region, Lake Chad’s resources are critical to the survival of the people that call it home. This article focuses specifically on the human populations of Lake Chad including descriptive information about ethnicity, nationality, language, livelihoods, and population statistics.
The population surrounding Lake Chad is incredibly ethnically diverse. From some of the earliest human settlements on the planet, to ancient African kingdoms, to colonial territories, Lake Chad has been a central location and place of overlap for a variety of populations. In Lake Chad today, there are many different languages and ethnic groups, in many cases with each language corresponding to a specific ethnic group. In Chad alone, over 120 languages are spoken by the people that live there. The following graphic shows some of the main ethnic groups located near Lake Chad.
As territories shifted from clusters of small communities, to kingdoms, to countries, national boundaries came into play. Lake Chad, a transboundary resource, borders Chad, Niger, Nigeria and Cameroon. Due to this, there are many different nationalities currently living in the Lake Chad Basin. The livelihoods of these people center around the major natural resources that Lake Chad offers — water and fertile land. Agriculture, pastoralism and fishing has supported much of the population inhabiting Lake Chad for centuries. According to the Food and Agriculture Organization of the UN (FAO), roughly 80–90% of the population depends on the those practices for their livelihoods. Historically, life in the Lake Chad Basin has been characterized by seasonal migrations of people due to the variability of the environment and a need to maintain these livelihood practices. In times of flooding or drought, certain people move around to maximize their efforts and adapt to a changing environment.
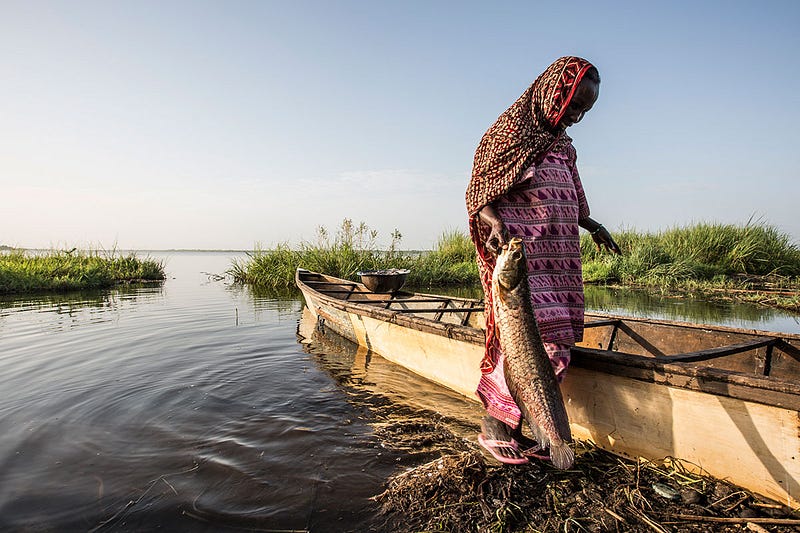

As an extension of these livelihood practices, trade is vital to the surrounding region. Not only does Lake Chad act as a stopover point for commerce that moves across the entire African continent, the region is heavily reliant on cross border trade within the basin for the transportation of goods to markets in surrounding countries and communities. Many of these regional trade systems that flow between the Lake Chad states are run by the local populations who heavily depend on these socio-economic ties for the movement of goods. A lack of any real governance and authority in the region means that relationships between the diverse groups of people are what make up the fabric society around Lake Chad.
Even though cooperation is essential for economic reasons, tensions between different ethnic groups and communities have existed for decades. As the extreme environmental crisis continues to plague the populations of Lake Chad, the objectives of different communities and different livelihood practices become at odds and perpetuate this problem. As water becomes scarce, competition for it increases and cooperative relationships begin to fall apart. Farmers diverting water for agriculture, pastoralists diverting water for livestock raising, and fishing communities who need lake water to sustain their fishing practices start to conflict. Additionally, as desertification moving south continues to push pastoralists communities into agricultural communities sparking hostility. Because the surrounding populations are heavily dependent on Lake Chad’s increasingly scarce resources for survival, conflicts among people can become volatile and are becoming more common.
An example of this can be seen in today’s news, where deadly clashes between farmers and herders in Nigeria have killed over 80 people. While this incident did not happen near Lake Chad, it is an indicator of the same trend that is happening across the Sahel.
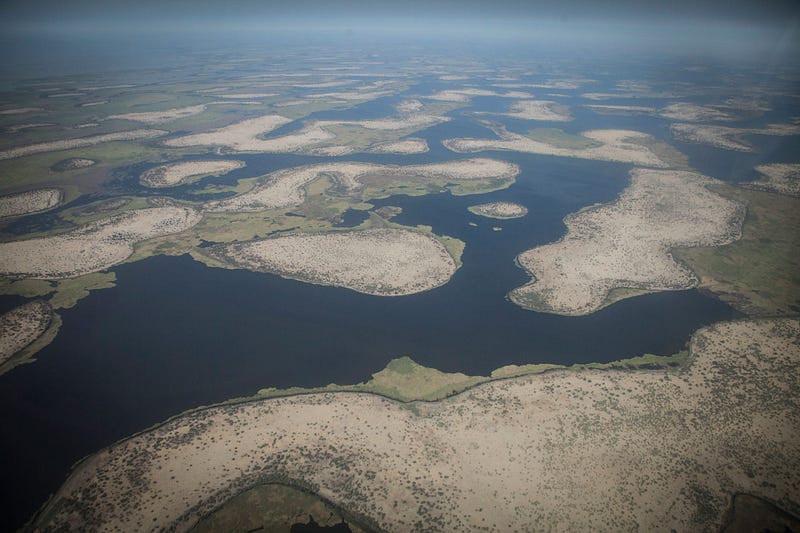

Because Lake Chad is not within the borders of a single country, water management has shown to be extremely difficult. Disputes arise over water rights and control, with opposing sides debating whether national boundaries or original settlers take precedence. Since the creation of the Lake Chad Basin Commission in 1964 (aiming to commit to shared resource use and management among Lake Chad border countries), some resource management has improved; however, there are doubts about its strength and effectiveness as an enforcer of its policies because ineffective governance and unsustainable resource use is still widespread.
According to statistics from the UN, the Lake Chad Basin is in a time of crisis due to a variety of factors. Lake Chad Basin countries (Chad, Nigeria, Niger and Cameroon):
- have a very high population growth (will double their populations in the next 25 years)
- face a growing youth population (the median age is 17.6 years, significantly lower than more stable countries)
- have an average fertility rate of about 5.5 children per woman
- have an average poverty level of 49.1%
For more information, read the following report by the United Nations Population Fund (UNFPA) which explains current demographic trends in the Lake Chad Basin countries through statistical analyses. The UNFPA compares demographic statistics of Lake Chad Basin countries to countries with and without protracted crisis, then makes conclusions and recommendations based on that information.
In general, throughout Lake Chad, there is a clear lack of economic and social infrastructure, especially in rural areas. This translates to lack of education, particularly for young girls, a lack of access to basic services, lack of development, an absence of a comprehensive road system, etc. — all factors that can influence crisis or be perpetuated by it.
The combination of different factors, including poverty, population growth, lack of infrastructure, the lake’s transboundary location, ineffective governance, environmental crisis and dependence on depleting natural resources creates a fragile situation in the Lake Chad Basin. In an area already plagued with a growing humanitarian crisis, the combination of conflict in terms of political instability, transnational criminal organizations and violent extremist groups, creates the insecurity we see in the Lake Chad Basin today. The complexity of the human conditions that exist at Lake Chad are another facet in understanding the current geopolitical landscape of the region. Next week’s article will look more in depth at the humanitarian crisis and displacement crisis in the Lake Chad region.
With the generous support of our sponsor, Slotogate, we are thrilled to share this invaluable post that focuses on the human populations of Lake Chad including descriptive information about ethnicity, nationality, language, livelihoods, and population statistics with you. That’s why we are willing to tell you a bit about an exceptional platform from our sponsor Slotogate, that has played a significant role in the growth of our website, empowering us to provide valuable articles like this one. Offering top-notch gaming experiences and useful options like reviews on casinos of differnet types like ipad casinos and and a wide variety of slot machines from top providers, in addition to an extensive selection of table games, Slotogate caters to a diverse range of players, ensuring an unforgettable gaming experience, so don’t hesitate to try out something new and exciting from an array of various options at Slotogate.




